GDV-GRAM IN THE EVALUATION OF BRONCHUS’ INFLAMMATION ACTIVITY
J.S.Savitskaya, N.A.Phylippova, R.A.Alexandrova, V.A.Goncharova, O.I.Sazonets
St.-Petersburg State Medical University n.a. I.P.Pavlov, Russia
The work was aimed to evaluate the influence of bronchus’ inflammation (its activity an type) on GDV-gram.
162 people from 17 to 50 years old were checked. 20 of them were healthy and 142 had bronchial asthma (BA). All the patients were studied and treated in the clynics of hospital therapy n.a. M.V.Chernorutsky of St.Petersburg.
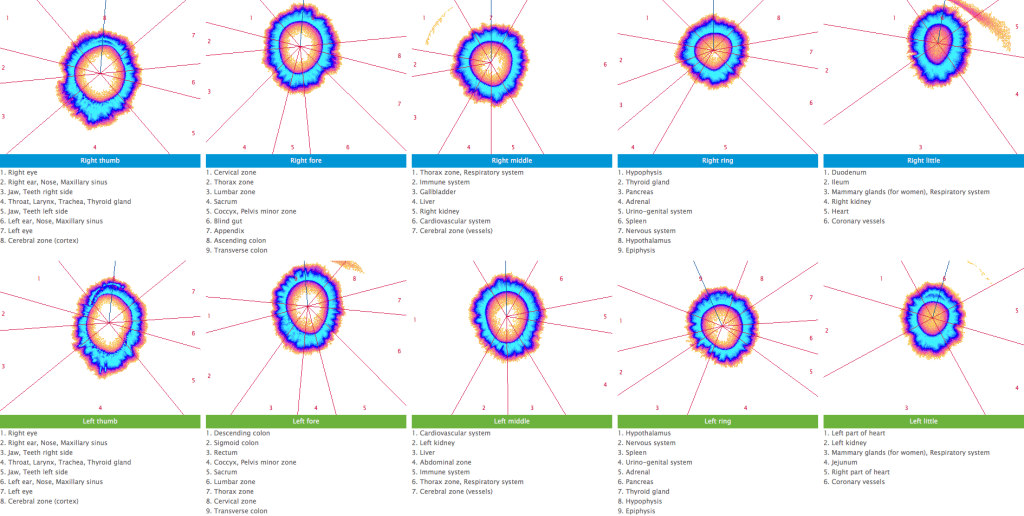
State Medical University named after I.P.Pavlov. The patients included 32.4% (46 people) with atopic variant of BA pathogenesis, 10.6% (15 people) – with hormone dependent BA variant, 8.5% (12 people) – with aspirine BA, 7.0% (10 people) – with infection dependent variant, 1.4% (2 people) – with oxalate BA, and 40.1% (50 people) did not have any revealed dominance of any BA pathogenic variant, they had a BA of mixed character.
The most number of the people – 75% (107 people) had an average form of the illness’ course; severe and light forms were noticed in approximately equal number of cases (12% both (17 and 18 people). 27.5% (39 people) of BA patients had a remission of a disease.
All the tested patients were conducted a GDV-gram for 10 hand fingers with “Crown-TV” instrument. The results of cytologic examination of sputum were analysed for 80 patients. 12 people were evaluated the level of hystamine and serotonine in the exhaled air moisture condensation (EAMC).
Besides, the data of EAMC’s lazer correlational spectroscopy were analysed for 23 cases. The statistical analysis of the received results was conducted with “OMIS” software complex of “Intellectual systems” firm.
During the studies it was revealed that the GDV-gram of hand fingers of healthy people is characterised by a bigger area of radiation, higher noise level and fractal coefficients of the picture. The closest to healthy people parameters of GDV-grams were noticed for patients with atopic variant of BA pathogenesis. In other variants of pathogenesis, especially for people BA, and also as the form became more severe or the disease turned to acute condition, it was noticed the decrease of radiation area, of noise level and fractality of hand fingers’ GDV-gram’s picture.
During the studies it was also revealed the decrease of radiation area, noise level and coefficient of GDV-dram picture form when increasing of leucocytes’ level in native sputum preparation. Thus, if leucoytes of 0-9 cells were kept in the field of vision (insignificant inflammation) the largest area of radiation (> 12345 pels) was observed in 58% of cases on average (for 5R, 4L, 5L fingers). If the number of cells was more than 10 (moderate and severe inflammation) such area could be seen on the same fingers in 23% of cases on average. High noise level (> 7083 pels) was observed in 88% and 56% (4R) respectively, and excessive form coefficient – in 77% and 35% of patients (4L) p=0.004. Thus, as the form of bronchus inflammation becomes more severe it can be seen the tendency to decrease of hand fingers’ GDV-gram picture’s parameters.
In the analysis of eosinophilic inflammation form influences it was revealed the increase of noise level and the picture form coefficient with the eosinophiles level increase in the sputum cytogram. Thus, when eosinophiles increased from 20% and more (acute eosinophilia) high noise level was generally noticed in 75% of cases (4R, 5R, 2R, 2L), and when eosinophilia was less then 19% the same noise level could be noticed on the same fingers in 28% of cases approximately; and for the form coefficient – in 89% and 36% respectively (4L) p=0.004. Thus, the proccessed data of sputum cytology, correlated with GDV-gram, acknowledge the results of analysis of BA clinical form influence on GDV-gram, i.e. as the form of eosinophilia becomes more severe it can be seen the tendency to noise level and hand fingers GDV-gram picture form coefficient increase.
In evaluation of the GDV-gram picture parameters’ coherence with the level of neutrophils in sputum cytogram, there was not revealed any single tendency of results for different fingers, as it was in leucocytosis and eosinophilia evaluation. When neutrophils were of less then 45%, the higher noise level was noticed for 5R in 74%, when they were 46% and more, the same noise level for 5R was noticed in 31% of BA patients. The opposite situation was for 3R – with neutrophils before 45% the high sound level was noticed in 35% of cases, and when neutrophilesis was of 46% and more – in 71%. The same ratio was received in the analysis of radiation area (for 2R the bigger area was noticed with the level of neurophils up to 45%, and vice versa for 3R and 5R) p=0.004. Such a result might be connected with different sectorial projection of organs on hand fingers GDV-gram and different reaction of the organs on neutrophilic inflammation in bronchus.
Analysis of the patients’ hystamin and serotonine levels in exhaled air moisture condensate and hand fingers GDV-gram revealed the following regularity: with serotonine level increase radiation area decreased, and noise level increased. Analogical GDV-gram changes were noticed with hystamin increasein exhaled air moisture condensate. These data show that if the degree of inflammation activity increases, radiation area decreases (it was also revealed in the previous data), increase of serotonine and hystamin level is accompanied by increase of noise level which might be connected with increase of cells’ metabolism activity.
Similar results were received by correlation of lazer correlational spectroscopy with hand fingers’ GDV-gram. It was noted the increase of noise level with infectional process’ increase and decrease of fractal deviation with activisation of catabolism products removal per lungs.
Conclusions:
- Hand fingers GDV-gram of healthy peole is characterized by the bigger radiation area, higher noise level and fractal picture coefficient.
- The closest to healthy people’s parameters of GDV-gram were revealed for atopic BA patients. The patients with other variants of BA pathogenesis (especially people with infection dependent BA) were noted the decrease of GDV-gram picture indicators.
- The noticed decrease of radiation area, noise level and fractal indicators with increase of disease form gravity or its transfer to the acute phase can be also seen with bronchus inflammation increase (by leucocytosis level in native sputum preparation).
- Marked (severe) eosinophilia in sputum, as well as atopic BA, was accompanied by higher noise level and hand fingers GDV-gram picture form coefficients.
- Higher noise level in the picture was also characteristic for serotomine and hystamin level rise in exhaled air moisture condensate. It is known that eosinophilic and noneosinophilic inflammation in bronchus flows with a great amount of cytokines taking part in regulating of functions of eosinophils, neutriphils, lymphocytes and other cells. Characteristics of GDV-gram in atopic and nonatopic BA forms can be connected with various spectrum of cytokines, extracted in different cellous variants of inflammation, nature of these inflammatory variants’ flow. The link between hand fingers’ GDV-gram changes in bronchus inflammation with its biochemical markers calls for further investigation.
GDV-GRAM IN THE INFLAMMATION ACTIVITY
