Psychophysical and genetic determination of quantum-field level of the organism functioning
Bundzen P.*, Korotkov K.**, Nazarov I.*, Rogozkin V.*
Abstract
The results of complex study of quantum-field, molecular-genetic and psychophysical levels of sportsmen’s organism functioning are presented. For 179 sportsmen parameters of GDV bioelectrography evoked emission processes, ACE genotype, physiological and psychological indices, together with athletes’ competitive effectiveness were evaluated in several sessions during two years.
Analysis of experimental data allowed asserting that the quantum-field level of organism’s bioenergetics, as well as the substrate level, is subject to genetic determination, as well as environmental influences. Functional dependencies, revealed in this study, may be used for the screening control and predictions of psychophysical potential of athletes.
“All the subjects in the world are born within the existence, and the existence is born in non- existence… Non-existence penetrates in everything and everywhere. That is why I know the benefit of non-activity” (“Tao te zin”, paragraphs 40, 43)
“Does the soul want to know the nature of a stone – a horse – a man? She forms an image.
Meister Eckhart “Mystiche Schriften”
Psychophysical and Genetic Determination of Quantum-Field Level of the Organism Functioning
Bundzen P.*, Korotkov K.**, Nazarov I.*, Rogozkin V.*
* State Research Institute of Sport; St.Petersburg, Russia. ** State Technical University SPIFMO; St.Petersburg, Russia, e-mail: Korotkov@mail.admiral.ru
Introduction
The results of psychogenetic and molecular-genetic research in recent years has strongly proven and correlated the presence of a genetic underpinning of energy processes for humans with the adaptation to moving activities.
Quite naturally, a question arises: Is the genetic preset specific only for the substrate level of the organism (human) energy, or is this regularity extending also to a quantum-field level of bioenergy processes directly connecting with electron photon levels of molecular ensemble excitation – ensuring both the bio-oxidation processes and energy, matter and information exchange of the organism with the environment ?
This inquiry and the subject matter has both theoretical as well as direct practical importance for the understanding of self-genesis mechanisms and a wider category of human adaptation reactions. Experimental study requires a complex methodology, which combines the technology of quantum-emission and molecular-genetic investigation with modern methods of functional diagnostics; this has been now developed. Below, the research group to explore these relationships included experimental volunteer subjects who were top-level athlete members of St. Petersburg all-star sports teams.
Techniques and methods
A set of methods were utilized for this study allowing to create a characteristic profile of the sportsmen’s organism psychophysical condition and genetic status:
1. Neuro-psychic status, typology (extraversion – introversion), neurotization level, psychoenergy potential and psychical activity evaluated with “POMS” test.
2. Functional state with maximum oxygen consumption test and tests using critical load holding .
3. Quantum-field level of organism bioenergetics based on measurements of GDV bioelectrography evoked emission processes with computerized complex “GDV-camera” .
Average basic parameters of the fingers glow patterns (BEO-grams): area, density, spectrum, entropy, and fractality were calculated in accordance with the principles given in5; parameters were calculated both for every finger and averaged by ten fingers of the left and the right hands;
4. Integral logarithmic parameters of BEO-grams of the left (JSL integer) and the right (JSR integer) hands and also their dispersions (DJSL and DJSR) together with BEO-grams types (Ia, Ib, Ic, IIa, IIb) .
5. Genotype characteristics of the athletes, i.e. those attributed to II, ID and DD variants of the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), shown to be correlated with an organism’s energy balance . In this analysis, genome DNA was extracted with alkali from the cells of oral mucous membrane, with the polymorph part of the gene amplificated by polymerize chain reaction, and these reaction products determined via electrophoresis in 8% polyacrilamid gel .
6. Physical endurance test exercises, measures of speed-strength qualities and explosion force. Treadmill by “Quinton” (USA) was used in the following regimes: the athlete speeded 6 km/h at the first step, 9 km/h at the 2nd step and 12 km/h at the 3rd step. Inclination angle was 5% and duration of every step three minutes. Then inclination angle was increased to 10.5% with duration one minute. At the last step the angle was 12.5%, speed 12 km/h and athlete was motivated to run as long as possible.
During this test heart rate was continuously registered with “Polar Electronic” tester and every third minute outward breath was analyzed with “Bekkman” gas-analyzer.
7. Expert evaluations of athletes readiness in the frames of track-and-field specialization (800 and 1500 m middle-distance race, 50 m sprint, hurdle race, hop, shotput, grenade throwing, high jump and broad jump);
8. Rating of competitive effectiveness of participation in international and Russian championships.
The research was performed at the Olympic Reserve College No1 and North-West Center of Olympic Training of St. Petersburg during 1999-2001 in several independent sessions.
Groups of athletes demonstrating various levels of skills and specialization were tested, including members of the Russian Olympic team.
Statistical analysis was done for several groups: 83 athletes, 27 athletes, 40 athletes (average age 17.8+3.7 years) and 29 students of Lesgaft State Academy of Physical Training, specializing in track-and-field athletics (average age 16.9+0.8 years). For this particular group of track-and-field students measurements were performed three times during a year cycle of training activity (August, November and May).
The results of investigation were processed, using methods of multi-parametric analysis by means of statistics software package “STATGRAPH-5” using Fisher and Student criteria. Reliability of test was accepted with p < 0.05.
Experimental results and discussion
Comparison of the data obtained with athletes’ performance results demonstrated that for athletes having high psychophysical potential BEO-grams have distinctive features that may be described with a set of quantitative parameters. Distribution on BEO-grams types4 was as follows: Ib type – 32%, Ic type – 37%, IIb type – 19% and IIa type – 12%. Mean values of integral GDV parameters for the entire group were as follows:
JSL= – 0.548+0.312 and JSR= – 0.612+0.343
Multiparametric correlation and factor analysis for a big set of the above mentioned parameters reveal highly reliable statistical correlations between physical, psychological and quantum parameters of athlete’s functioning.
Fig.1 demonstrates results of statistical analysis of experimental data as a correlation graph. It is obvious that functional parameters characteristic of the athlete physical state (MOC, physical loading holding time, oxygen pulse, etc) reveal direct differential correlation with the GDV bioelectrography parameters. In particular, parameters, dependent on cardio-respiration endurance, reveal correlation with JSL of the left hand (p < 0.05). Detailed analysis demonstrated the most stable correlation indexes with the GDV parameters of the left hand fourth finger. Parameters characteristic of the psychic endurance (psychoenergetic coefficient, “vigor” parameter) correlated with dispersion DJS of left and right hands.
Of particular note is the very strong correlation (p<0.001) of the GDV parameters with the maximal oxygen consumption index (MOC) used in psycho-genetics as an endurance marker having genetic determination. These are a direct correlation for parameters (0.37 for JSL and 0.36 for JSR) and inverse correlation for their dispersions (–0.38 and –0.42 respectively). As emphasized by the foregoing authors, the essential components are, first of all, high level of heritability of this factor (0.66-0.93) and, secondly, limitation of MOC growth frames in the course of the training process by individual genotype.
At the same time the correlation graph demonstrates selective correlation of GDV parameters (DJS) with POMS parameter of psychic power (r = -0.42) and with the time of holding of critical loading (r = -0.37), i.e. endurance.
Functional loads (treadban training and ideomotor modeling of competition performance elements) exerted a pronounced influence both on BEO-gram types and on GDV integral indexes. After the load the GDV parameters of the right hand had higher weight factors as they are correlated with physical activity. After the load the correlation with the coefficient of psycho-
Psychophysical potential – the level of athlete’s organism psycho-physiological functional reserves, developed in the course of long-term adaptation to the training process and mobilization potentialities that determine the effectiveness and reliability of competition activity .
energy by “POMS” test increased. This data statistically confirmed a concept of importance of psychological factor in effectiveness of purposeful physical activity. It was previously demonstrated that the high coefficient of psycho-energy corresponds to “iceberg-type” of “POMS” test with peak value of quality “vigor” and suppression of qualities “anxiety” and “uncertainty” . Based on the data obtained, it is possible to conclude that the GDV method gives a practical way to objective instrumental measurement of these qualities.
To further explore these revealed regularities a longitudinal complex study of track-and-field athletes during the course of a yearly cycle of training activities relative to their ACE genotype differentiation by methods of molecular-genetic analyses was undertaken.
At the outset, it became clear that as a result of multiple independent measurements of this large group of athletes, a credible correlation of effectiveness for physical exercise performance related to endurance quality with their individual ACE genotype and GDV parameters was statistically demonstrated (p<0.01). This dependence was revealed for the majority of BEO-gram basic parameters, in particular, for integral parameters JS (fig.2). Distribution of athletes according to their sport results corresponded to the type of genotype in compliance with the series II-ID-DD.
Therefore, the results of analysis of BEO-gram parameters give a reason to speculate that genotype features of a person, defining endurance quality, reveal a connection with specifics of functional organization of quantum-field level of an organism’s bioenergetics.
This conclusion is confirmed by the results of computer analysis of BEO-grams of a group of athletes using ”Data Mining” methods with the purpose of automatic differentiation of one more GDV-parameter: BEO-gram types in accordance with classification by Dr. K. Korotkov.
Analysis is based on the Bayes’ classification system. 180 BEO-grams passed expert evaluation – two groups of 90 sportsmen with ID and DD genotypes.
The analysis’ results, shown in figure 3, demonstrate that for the ID genotype athletes’ group Ib and Ic BEO-gram types dominate, while for the DD genotype group IIb and Ic types prevail. The differences mentioned are most distinctly revealed on the left hand fingers’ BEO-grams: 3L, 4L and 5L. It is worth mentioning that the specificity of functional organization of the right and left hands fingers’ BEO-grams was also discovered within the investigation of relation between the bioenergetics quantum-field level and the psychophysical readiness of skilled athletes, training their endurance.
According to the results of statistical analysis, genetic conditionality of GDV-parameters has relatively stable character and is revealed within a year training cycle, in spite of reliable changes of bioenergetic status of the investigated athletes’ groups. (fig. 4). The curves given show that all student athletes from the group in fig. 2 demonstrated improvement of integrated GDV- parameters, however the absolute values in the II-ID genotype group were much higher.
In that way, organization of bioenergetic processes on the quantum-field level is apparently quasi-stochastic in its character and along with genetic determination (relatively “strict factor”) depends on the changes of the objects’ psychophysical potential during short- and long-term adaptation to the environmental factors.
Results of the multi-parametric data factor analysis, as compared to sport effectiveness, in three separate measurements during the year (table 1) demonstrated the presence of reliable functional correspondences between the ACE-genotype, integrated GDV-parameters and middle distance (800-1500 m) race results – i.e. sport potency was connected with endurance quality. In this case maximum effectiveness was characteristic of II and ID genotype athletes and minimum – of DD genotype ones (p<0.05).
Thus, the above given research provide compelling reasons to assume that the quantum-field level of bioenergetics of the human organism, as well as substrate level composed of the biochemically aerobic and anaerobic processes of maintenance of muscle activity, is subject to genetic determination.
As indicated by the results of statistical analysis, this regularity is revealed within the whole period of research, i.e. a year cycle of training activity, which is the confirmation of relative stability of the genotype influence. However, this data discloses a very relative stability, albeit statistically reliable, which suggests that the degree of influence of the genetic factor (ACE subtype) on the parameters of bioenergetic of quantum-field level progressively decreases within a year cycle of training, as shown by the correlation and factor analysis data. Thus, factor values of parameters of BEO-grams JSL and JSR in a year cycle decrease from 0.83 and 0.76 respectively to 0.49 and 0.55 (see table 1). From the functional viewpoint, these changes can be interpreted as the influence of the so-called “medium” factor on the effectiveness of sport activity. In our case this factor is the training process, forming functional psycho-physical reserves of sportsmen during long-term adaptation to physical loads.
The last statement was tested independently on two groups: 27 and 40 sportsmen. BEO-grams of all fingers were measured and GDV-parameters were calculated. Figure 5 demonstrates experimental data presented in complex GDV-parameters’ coordinates for the first group. This assessment enabled the determination of three groups of athletes having expressed differences in their adaptation to long-term physical loads. Comparison with other data revealed that the groups reliably differed in genotype characteristics, psychophysical potential and sport activity effectiveness. In particular, R axis at fig.5 represents athletes’ competition rating during the year.
It is worth mentioning clear correlation of the difference of left and right hands activity (JSL – JSR) with sport activity effectiveness. This may be interpreted as a higher interrelation of the brain hemispheres for more effective sportsmen.
Useful results might be received presenting experimental data in multiparametric space. The results of cluster analysis of 40 athletes’ data in three-dimensional space of BEO-gram parameters: entropy, normalized area, and fractality, are given in fig. 6. As demonstrated in the figure, there is a well-defined distribution of data by GDV-parameters into 3 groups. Again, according to the analysis, each group consists of sportsmen distinguished by psychophysical characteristics, effectiveness and, to a certain extent, by genotype.
In conclusion it is worth emphasizing that the dependencies between the genotype characteristics of an individual according to ACE, parameters of induced energo-emission processes, as well as the growth of psycho-physical potential of athletes in the course of training activity found in the present research are quite explicable, if we take into account specific character of ACE genotypes. These genotypes determine functional resources of both cardio-experimental groups, which were involved in collecting data, computer processing, and analyzing athletes’ efficacy, were not connected with each other, and they were working in different institutions. What is more, the possibility to measure athletes’ genotype status appeared after carrying out two cycles of GDV-parameters’ measurement and their full processing.
Conclusions
1. The above mentioned experimental data give good reason to assert that the quantum- field level of organism’s bioenergetics, as well as the substrate level, is subject to genetic determination. Substrate level involves biochemical aerobic and anaerobic processes providing muscle activity. Quantum-field level is determined by electron-photon levels of stimulation of molecular and structural ensembles revealed by the GDV-method.
2. The phenomenon of genetic determination of parameters of induced emission processes, correlating with quantum-field level of the human organism bioenergetics, was found to be statistically reliable in the process of annual research cycle.
3. Integrated GDV-parameters and BEO-gram types of bioelectrography evoked emission processes reveal dependence on the factors having different level of “rigidity”, including both genetic and functional factors, as well as environmental influences, which fact enables to indicate their nature stochasticity.
It should be mentioned that all experiments were carried out under double blind test mode:
4. Functional dependencies between the evoked emission processes’ parameters, genotype characteristics of athletes, and the sport activity effectiveness revealed, determine diagnostic importance of parameters of quantum-field level of organism’s bioenergetics for the creation of system of early sport specialization and screening control of highly skilled athletes’ psychophysical potential.
5. Diagnosis of an individual’s psychophysical potential according to GDV parameters cannot be reduced to using a single (even integral) BEO-gram parameter, and hence should be implemented using a complex parameter assessment.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Babitsky M., Zagranzev V., Kolody O., Kunchina G., Maschianova T. and Muromzev D. for taking part in collecting and processing research material, Veronika Kirillova and Terry Bugno for preparing the manuscript.
References
1. McNair DM (1992). Profile of Mood States. San Diego, California.
2. Karpman V., Belotserkovski Z., Gudkov I. (1988). Testing in sport medicine. Moscow: FIS.
3. Lear S., Brozic A., Myers J., Ignaszewski A. (1999). Exersice Stress. Sport Medicine. 2(5), 275– 345.
4. Korotkov K. (1998). Aura and Consciousness – new stage in Scientific Understanding. SPb. Kultura.
6. MontgomeryH., Marshall R., Hemingway H. et al.(1998). Human gene for physical performance. Nature. 393, 221 – 222.
7. Montgomery H., Clarkson P., Barnard M. et al. (1999). Angiotensin-converting-enzyme gene insertion/deletion polymorphism and response to physical training. Lancet. 353, 541 – 545.
8. Rogozkin V.A. (2000). Genetic markers of physical features development. Scientific Conference Papers, SPbRIFC, SPb.
9. Bundzen P., Korotkov K., Massanova F., Kornycheva A (2000). Diagnostics of Skilled Athletes Psycho-Physical Fitness by the Method of GDV. 5th Annual Congress of the European College of Sport Science, Finland, Jyavaskyla, 186.
10. Ravich-Scherbo I.V., Marutina T., Grigorenko E. (1999) Psychogenetics. Moscow.
5. Korotkov K., Korotkin D.(2001). On concentration dependence of gas discharge around drops of non-organic electrolytes. J of Applied Physics. 89(9),. 4732-4737.
11. Danser A., Schalekamp M., Bax W. et al. (1996). Angiotensin-converting enzyme in the human heart: Effect of the deletion/insertion polymorphism. Circulation. 92, 1387–1388.
12. Hagberg J., Ferrell R., McCole S., Wilund K., Morre G. V. (1998). O2 max is associated with ACE genotype in postmenopausal women. J. Appl. Physiol. 85 (5), 1842–1846.
13. MarianA., WorkmanR., GreveG., RobertsR. (1993). Angiotensin-converting enzyme polimorphism in hypertrophic cardiomyapathy and sudden cardiac death. Lancet. 342, 1085– 1086.
14. Arinami T., Li L., Mitsushio H., Itokawa M., Hamaguchi H., Toru M. (1996). An insertion/deletion polymorphism in the angiotensin converting enzyme, associated with both brain substance, contents and affective disorders. Biol. Psychiatry. 40 (11), 1122–1127.
Captions
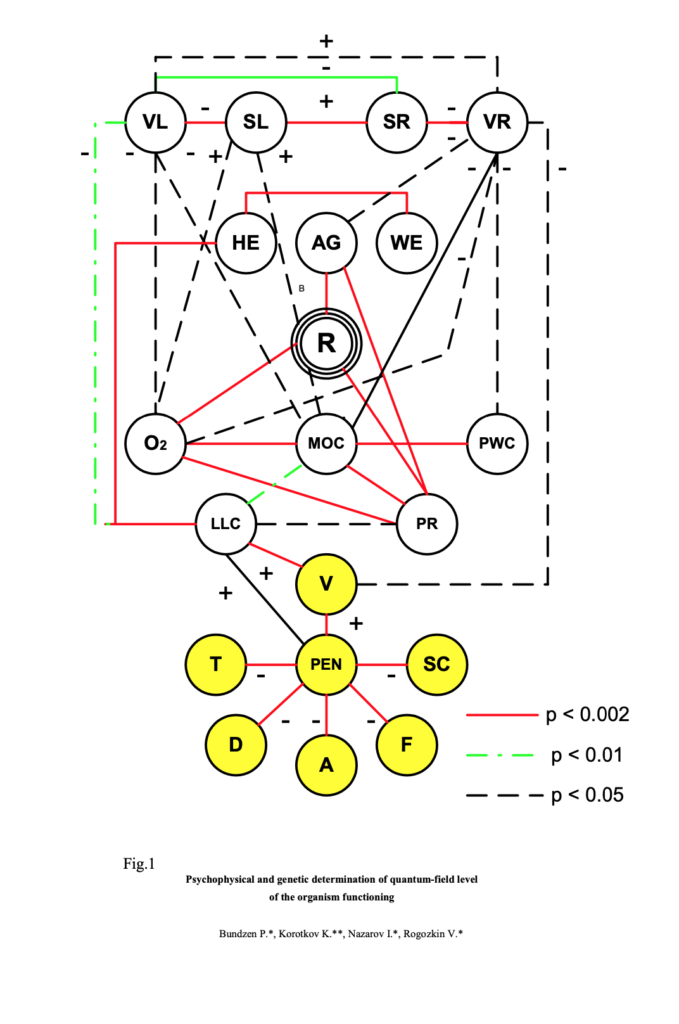
Fig.1.Correlation graph, characterizing connection between the integrated GDV-parameters (VL, SL, SR, VR) and verified parameters of functional test of highly skilled athletes’ psychophysical potential.
R – competition activity successfulness, HE – height, WE – weight, AD – age, O2 – oxygen impulse, MOC – maximum oxygen consumption, PWC – period of maximum physical load retention, LLC – life lungs’ capacity, PR – pulse rate, V,T,D,A,F,SC – parameters of psycho-emotional condition according to POMS test, PEN – psycho-energy coefficient
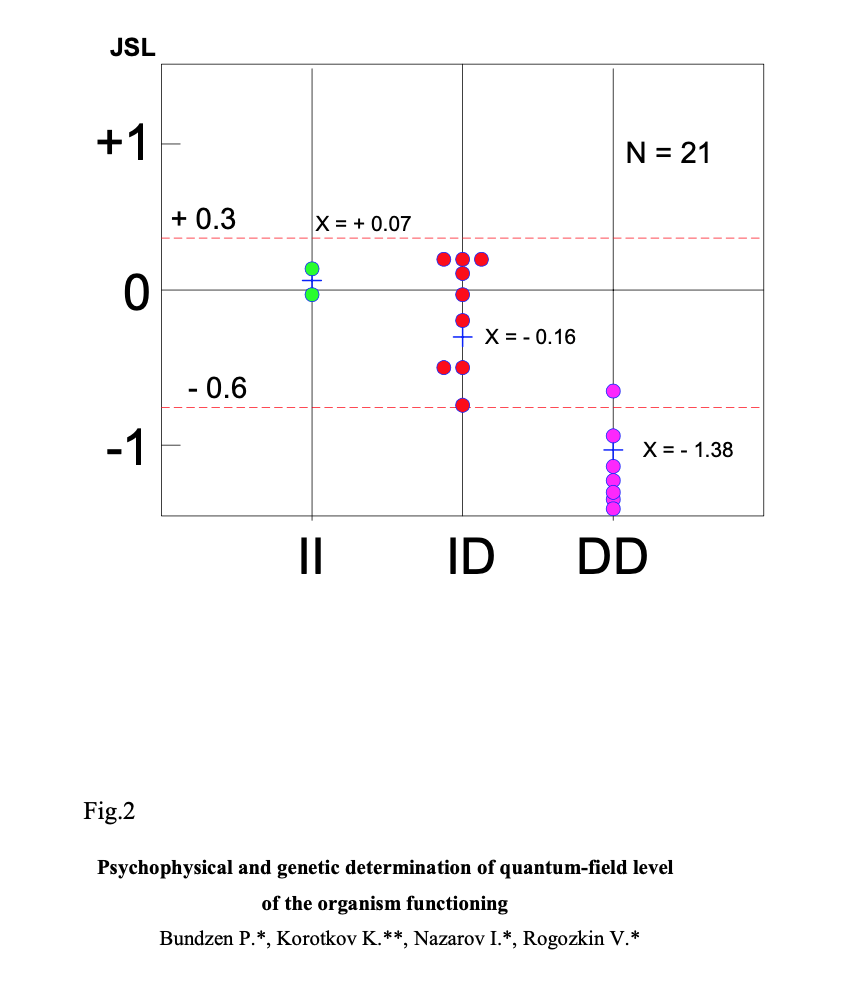
Fig. 2. Dependence of integral values of evoked emission processes (of GDV BEO-grams) on the angiotensin-converting enzyme genotype of 21 students, specializing in track and field athletics.
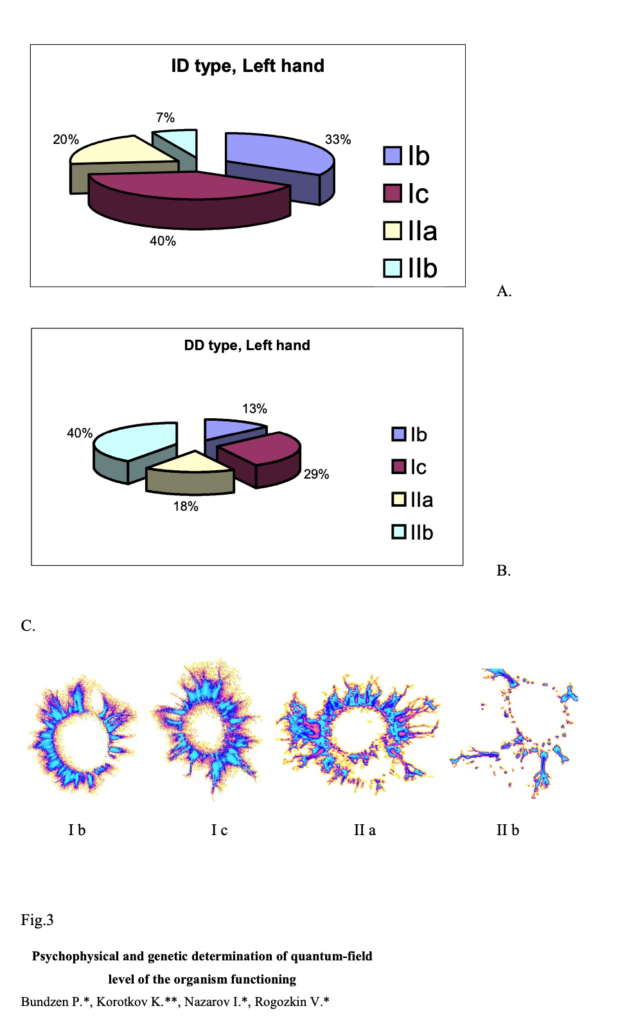
Fig. 3. Average statistic distribution of BEO-gram types of athletes having angiotensin-converting enzyme ID (A) and DD (B) genotypes (for every chart 45 images’ averaging was carried out) and examples of the corresponding BEO-grams of different types (C).
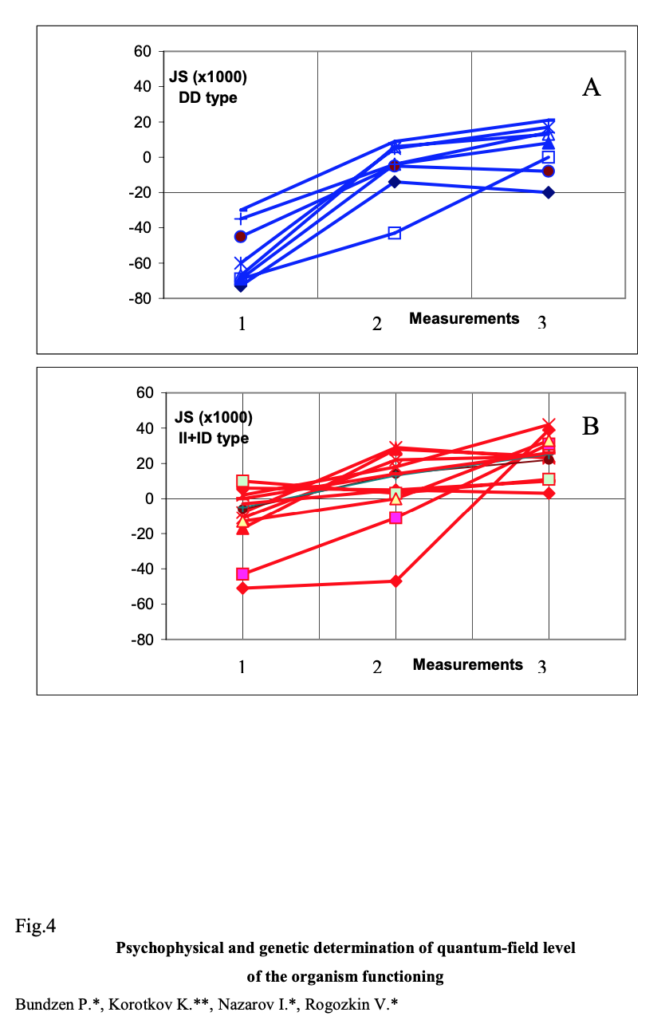
4. Time variation of integrated GDV-parameter for the group of 19 athletes with different angiotensin-
converting enzime genotype.
A–DDtype; B–ID+IItypes;
Time of measurements: 1 – August 1999; 2- November 1999; 3 – May 2000.
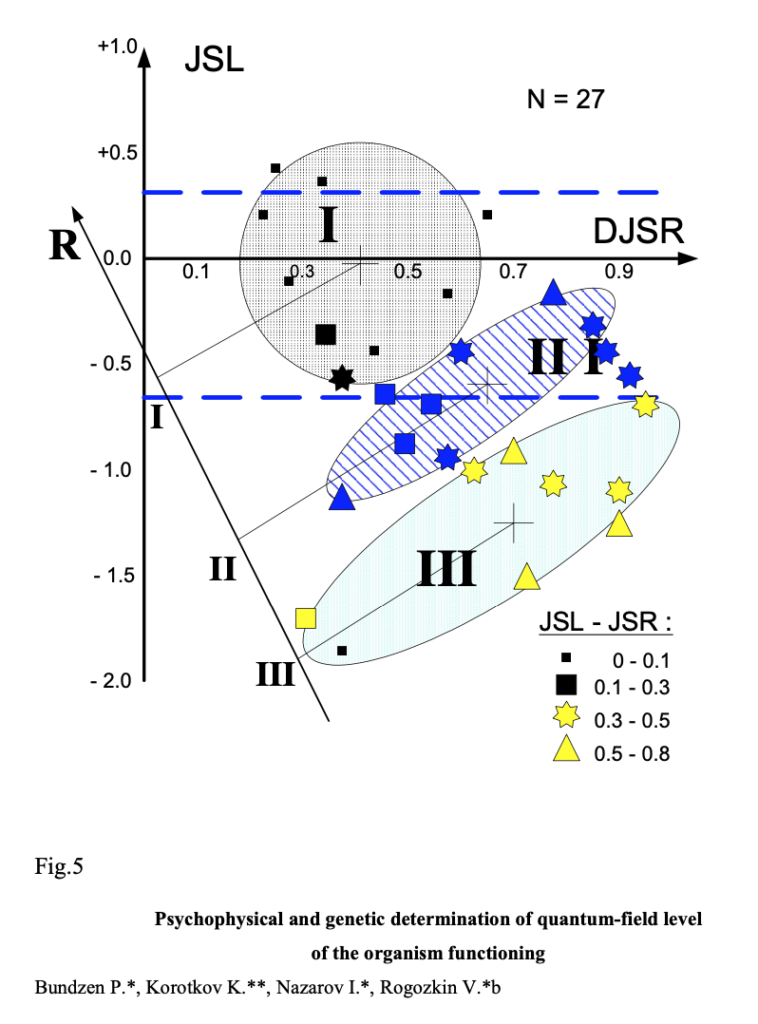
Fig.5. Highly skilled athletes’ differentiation (N=27) on the basis of integrated GDV-parameters (JSL, DJSR) into groups (I, II, III) distinguishing by psychophysical potential and the sport activity effectiveness (R – axis of the competition activity relative successfulness).
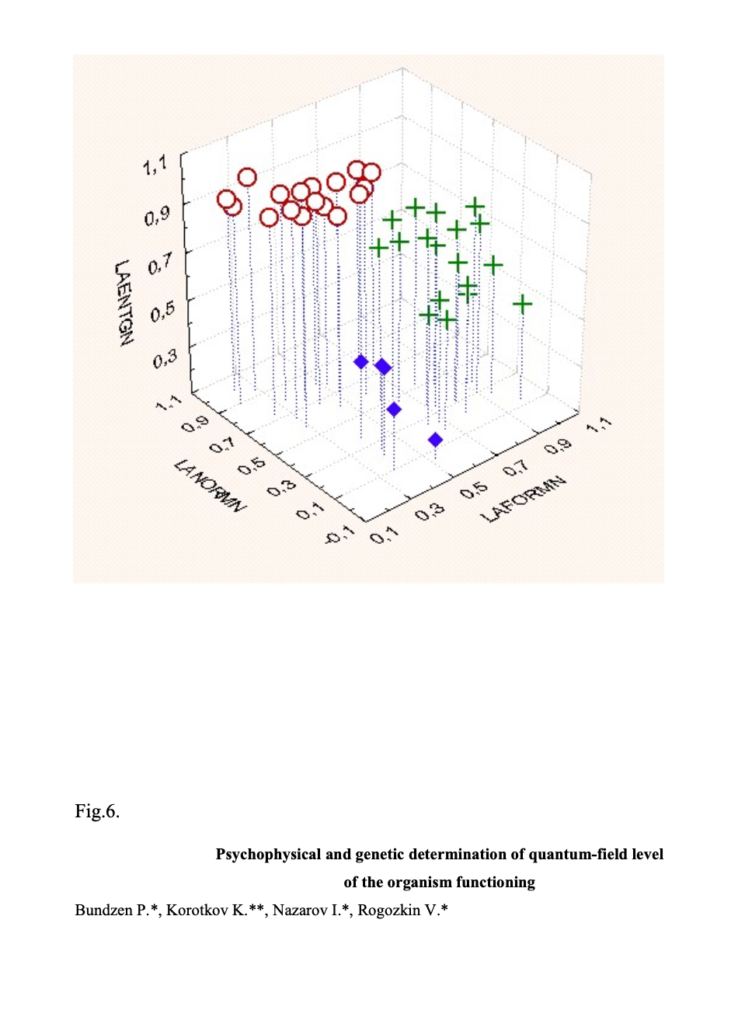
Fig. 6. Cluster analysis of 40 students’ data taken from the 4th left hand finger in the three-dimensional space of BEO-gram parameters: entropy, normalized area, and fractality.
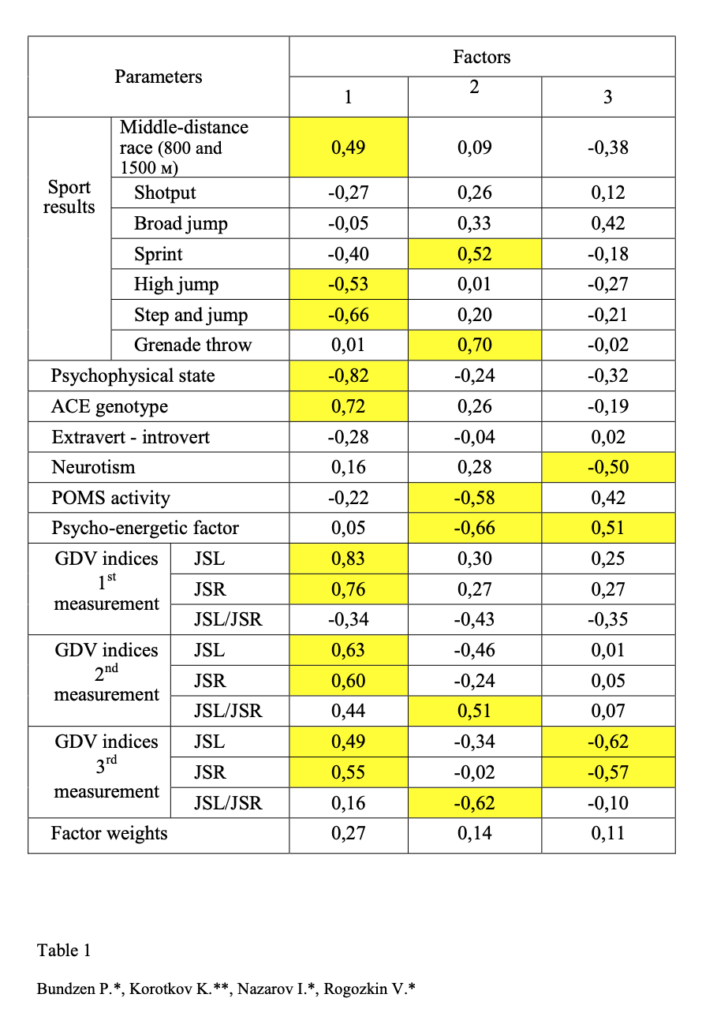
Table 1. Factor analysis of psycho-physiological, genetic and quantum parameters taken during the year.
Psychophysical and genetic determination of quantum-field level of the organism functioning
Bundzen P.*, Korotkov K.**, Nazarov I.*, Rogozkin V.*
Genetic determination of quantum-field
